Senegal’s economy recorded a significant rebound in 2024, growing by 6.1% compared to 4.3% in 2023, according to the Summary of the Joint Annual Review (RAC 2025) report released by the Ministry of Economy, Planning, and Cooperation.
The document, prepared in collaboration with the General Directorate of Planning and Economic Policies (DGPPE) and the Planning and Evaluation System Coordination Unit (UCSPE), outlines strong performance across several strategic sectors.
The report notes an 8.4% rise in GDP per capita, reaching 1,069,904 CFA francs in 2024. Inflation remained low at 0.8%, driven by falling prices of local products. The current account deficit also improved sharply, representing 12.5% of GDP, compared to 18.9% the previous year.
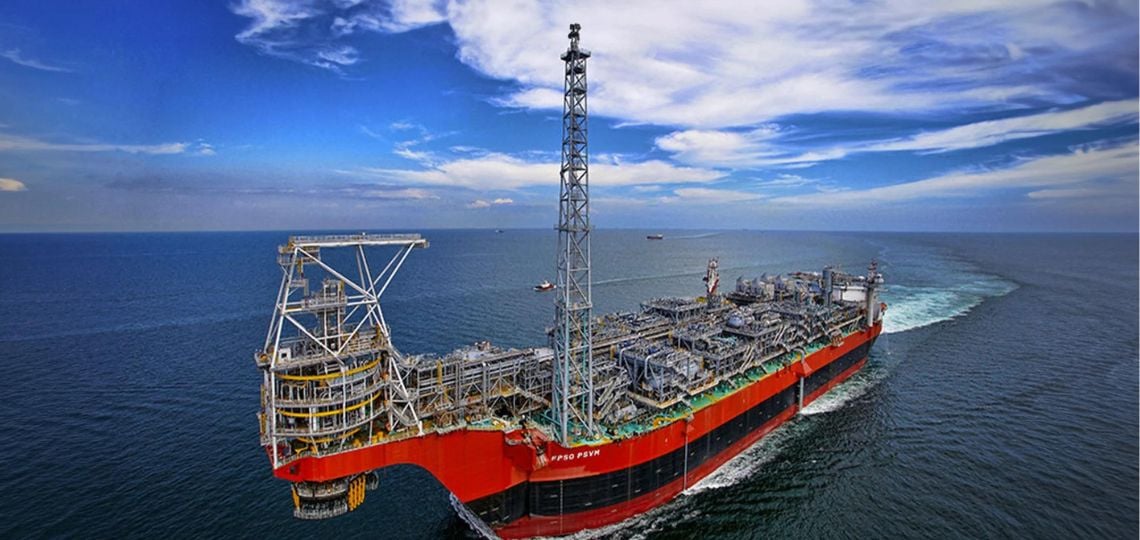
A major boost came from the extractive sector, following the start of oil production at the Sangomar field in June 2024, which generated nearly 595 billion CFA francs. Natural gas output, launched in December in the area shared with Mauritania, reached 4.36 million Nm³, propelling the sector to an exceptional growth rate of +187.5% compared to 2023.
However, agriculture faced a challenging year due to adverse weather conditions, including prolonged dry spells and floods. Cereal production dropped to 2.31 million tonnes from 2.6 million in 2023, covering just 48% of national needs. Rice output reached 946,209 tonnes, or 30% of consumption requirements, while peanut production fell to 795,585 tonnes. Despite this, horticultural output rose by 3%.
The energy sector continued its expansion, with an installed capacity of 1,903 MW and an electricity access rate of 86.02%, including 69.84% in rural areas. Renewable energy accounted for 28.8% of the national mix.
Social indicators also improved, with assisted deliveries rising to 97% and PENTA-3 vaccination coverage reaching 77%. The Single National Register (RNU) expanded to 954,571 households — a 76.4% increase over the previous year. Access to drinking water reached 98.6% nationally, while sanitation coverage improved to 73.6%.
Fiscal management also strengthened, with the budget deficit reduced to 13.4% in 2024 from 14.8% in 2023, supported by better spending controls and higher tax revenue. Senegal’s removal from the FATF grey list marked a milestone in its financial transparency efforts.
In employment, 77,870 new contracts were registered in 2024, though unemployment remains high at 21.3%. The activity rate stood at 57.9%, with an occupancy rate of 45.6%.
The RAC 2025 report concludes that “the achievements recorded must be consolidated through the implementation of the National Development Strategy (SND 2025-2029),” aiming to enhance governance and place Senegal “on a trajectory of sustainable and competitive development.”