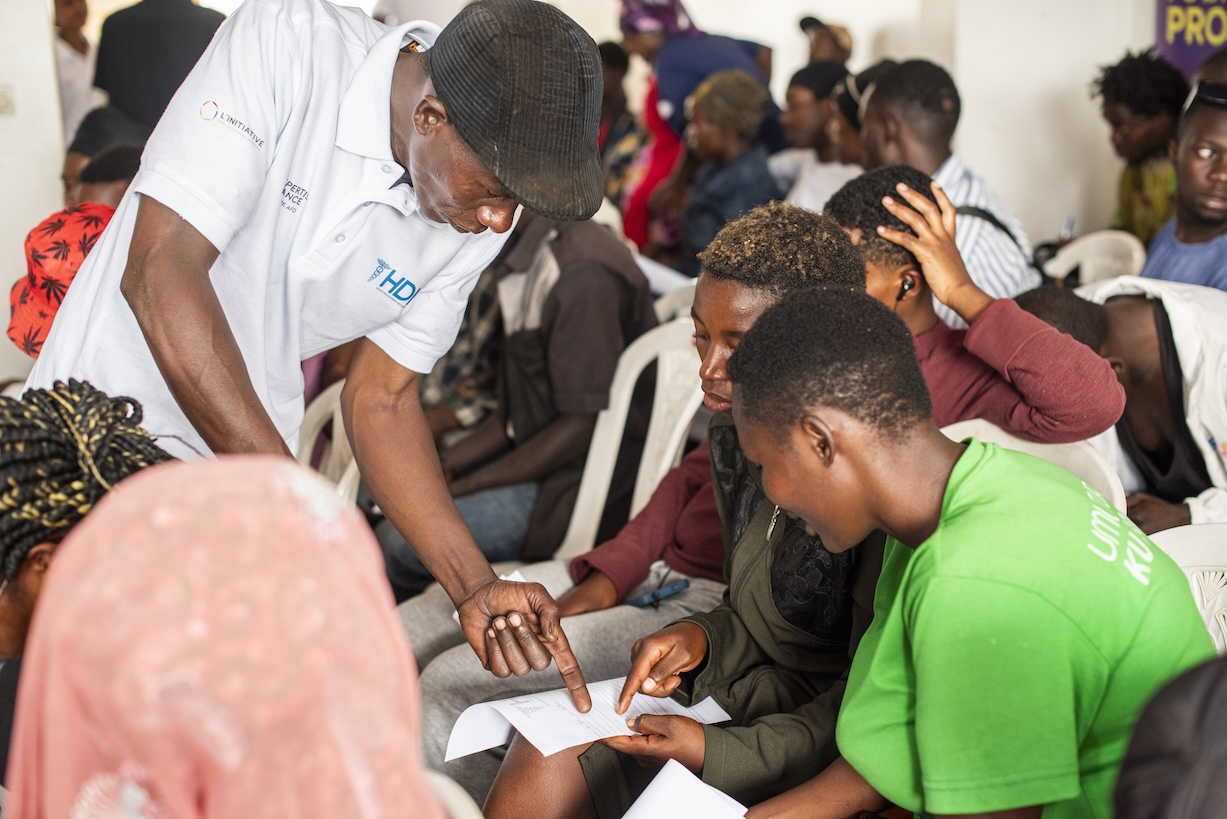
December 2024, Kigali, Rwanda, Expertsie France, L'Initiative, AFD, HDI, outreach center, SIDA, TUBITEHO Project, testing, drugs
The Directorate of Community Health and Health Promotion (DSCPS) in Ivory Coast has successfully organized two key multisectoral meetings aimed at enhancing the transparency and impact of community-based activities in the fight against HIV, tuberculosis, and cervical cancer.
These critical discussions were held on October 8 and 9, 2025, in Daloa, bringing together stakeholders from across the healthcare and social sectors.
The meetings, which attracted around 80 participants, were attended by a diverse group of health workers, NGO representatives, community leaders, local authorities, and technical and financial partners.
The initiative was supported by the NGO I-Tech Côte d’Ivoire and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), further reinforcing the collaborative nature of the event.
The sessions provided a platform for presenting the results of clinical and community interventions.
Discussions highlighted both the successes and challenges in the ongoing efforts to combat these three major health concerns.
Participants worked together to identify best practices, pinpoint areas for improvement, and offer recommendations for future actions to strengthen coordination and enhance the effectiveness of community health initiatives.
One of the primary objectives of the meetings was to foster open dialogue and accountability among the various stakeholders.
By creating a space for discussion and feedback, the DSCPS aims to improve collaboration between health facilities, communities, and health action partners, thereby promoting better local health governance and building public trust in the health sector.
HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and cervical cancer remain significant public health challenges in Ivory Coast, with high morbidity and mortality rates.
According to recent data, cervical cancer was the second most common cancer among women in the country in 2020, with over 2,000 new cases reported. Furthermore, the prevalence of tuberculosis/HIV co-infection continues to pose a serious threat, with a mortality rate of 20% in 2021, while nearly 401,000 people are living with HIV in the country.
The DSCPS emphasized the importance of these multisectoral meetings in driving forward meaningful change. By working collaboratively and ensuring accountability, the government and its partners aim to improve the health outcomes for those most affected by these diseases, ensuring a more coordinated and impactful approach to community health.